The route from the DNA code to
the protein.
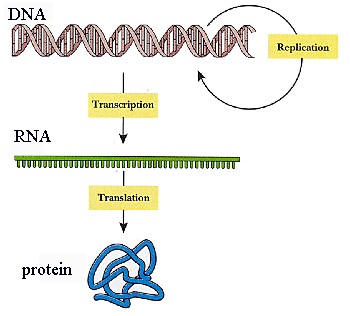
Before cell division, the DNA in our chromosomes replicates so each
daughter cell has an identical set of chromosome.
In addition, the DNA is responsible for coding for all proteins.
Each amino acid is designated by one or more set of
triplet nucleotides. The code is produced from one strand of the DNA
by a process called "transcription". This produces
mRNA which then is sent out of the nucleus where the message is translated
into proteins. This can be done in the
cytoplasm on clusters of ribosomes, called "polyribosomes". Or
it can be done on the membranes of the rough
endoplasmic reticulum. The cartoon to the left shows the basic
sequence of transcription and translational events.
http://cellbio.utmb.edu/cellbio/ribosome.htm
